The following suggestions are for informational purposes only. For official IRS instructions on how to fill out a W-2 form, go to www.irs.gov/forms-pubs/about-form-w-2.
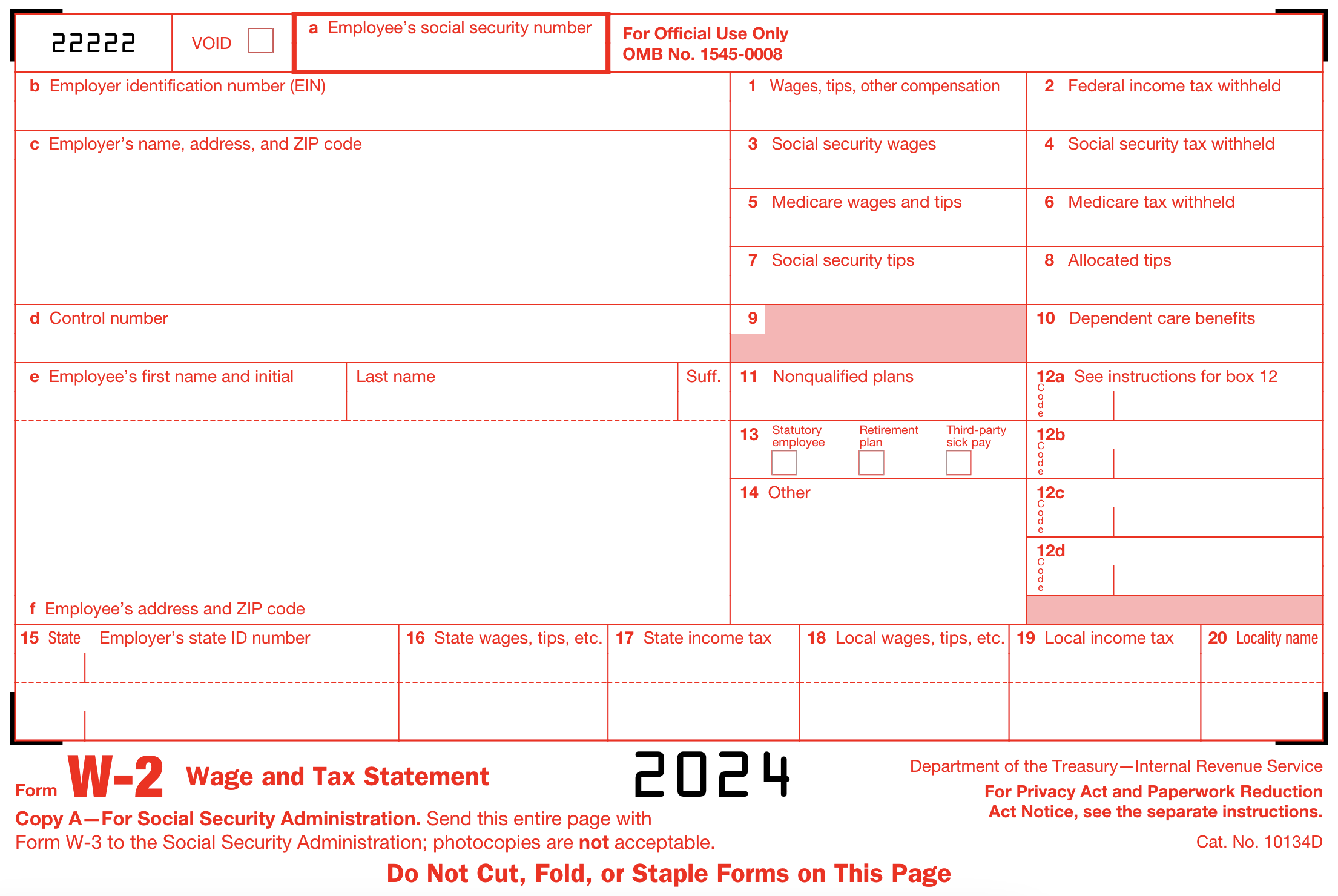
Descriptions of W-2 boxes
- Box A: Employee’s Social Security number
- Box B: Employer Identification Number (EIN)
- Box C: Name, address, and zip code
- Box D: Control number
- Box E: Employee’s name
- Box F: Employee’s address
- Box 1: Wages, tips, other compensation
- Box 2: Federal income tax withheld
- Box 3: Social Security wages
- Box 4: Social Security tax withheld
- Box 5: Medicare wages and tips
- Box 6: Medicare tax withheld
- Box 7: Social Security tips
- Box 8: Allocated tips
- Box 9: (Blank)
- Box 10: Dependent care benefits
- Box 11: Nonqualified plans
- Box 12: Codes
- Box 13: Checkboxes
- Box 14: Other
- Box 15: State | Employer’s state ID number
- Box 16: State wages, tips, etc.
- Box 17: State income tax
- Box 18: Local wages, tips, etc.
- Box 19: Local income tax
- Box 20: Locality name
Wondering how to fill out a W-2 form for an employee? This hands-on guide cuts through the complexity to provide you with a straightforward, step-by-step approach to complete each section.
Avoid common mistakes as we walk through some of the essentials of W-2 preparation. From understanding taxable wages to getting the crucial details right, we’ve compiled some helpful tips.
What is a W-2 Form?
At its core, the W-2 form, also known as the Wage and Tax Statement, is a comprehensive document that outlines the wages paid to employees and the taxes withheld from them. It’s essential for both employers and employees, serving as a reference point for annual tax returns.
The information provided in the W-2 form includes
- An employee’s wages earned throughout the year
- Taxes withheld from the employee’s paycheck
- Other compensation or benefits offered to the employee throughout the year
This comprehensive document helps the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) determine whether the employee is eligible for a tax refund or owes additional tax.
Understanding the W-2 form is crucial for accurate reporting and efficient tax return processing. It’s not just a form; it’s an employer’s tax guide and an employee’s roadmap to understanding their paycheck and the tax that’s withheld from it.
Filling out Form W-2
Filling out a W-2 form may seem daunting, especially considering the importance of accurate tax reporting. However, it doesn’t have to be a nerve-wracking process.
When completing the forms, whether on your own or with help from payroll software or a W-2 form generator, understanding the details of the W-2 form can simplify the process and support better tax form management overall.
The W-2 form contains several boxes, each for a distinct piece of information:
- Identification
- Taxable wages
- Taxes withheld
- Benefits information
The key is to be meticulous when filling out these boxes to ensure accurate tax reporting.
When W-2s are sent out
Before we delve into the specifics of each box, it’s important to note that the employers are required to provide each employee with a W-2 form by January 31 of the following year. This allows employees ample time to file their tax returns before the April 15 deadline.
W-2 Box A: Employee’s Social Security number
This number is used by the Social Security Administration (SSA) to track the earnings history of workers and determine their future benefits. Box A is the primary identifier for tax reporting.
W-2 Box B: Employer Identification Number (EIN)
Just as an employee is identified by their Social Security number, an employer is identified by an Employer Identification Number (EIN). This unique nine-digit number is assigned by the IRS to businesses for tax reporting purposes.
W-2 Box C: Name, address, and zip code
Box C of the W-2 form requires the legal name and address of the employee.
W-2 Box D: Control number
The control number is a unique identifier generated by your company’s payroll processing software. This number identifies each employee’s W-2 form in the company’s records, providing a point of reference in case of errors or discrepancies.
W-2 Box E: Employee’s name
This is the name that will be referenced in all tax documents and records.
W-2 Box F: Employee’s address
The employee’s current address is entered in Box F.
W-2 Box 1: Wages, tips, other compensation
Box 1 reports all taxable wages, salary, fees, bonuses, and tips, except for pre-tax benefits. This figure is determined by subtracting pre-tax deductions from the employee’s year-to-date gross income.
W-2 Box 2: Federal income tax withheld
Box 2 reports the total amount of federal income tax withheld from an employee’s paycheck throughout the year. This is the amount that was deducted from the employee’s income over the year and paid to the federal government on their behalf as federal income tax withholding.
Pro Tip
It’s essential to understand the difference between federal income taxes and federal income tax withholding to ensure accurate reporting.
W-2 Box 3: Social Security wages
Social Security wages are reported in Box 3. The total amount is reduced by certain pre-tax deductions but not retirement plan contributions.The Social Security wage base limit is the maximum amount of an employee’s income that can be taxed for Social Security purposes.
W-2 Box 4: Social Security tax withheld
Social Security tax withheld is reported in Box 4. The rate of this tax is 6.2 percent of wages up to the wage base limit.
W-2 Box 5: Medicare wages and tips
Medicare wages and tips are reported in Box 5. These are calculated using the same method as for Social Security wages but without a wage base limit.
W-2 Box 6: Medicare tax withheld
Box 6 is reserved for reporting Medicare tax withheld.
W-2 Box 7: Social Security tips
In Box 7, report tips that employees have reported to you. It’s important to note that these reported tips must also be included in the calculations for Boxes 1 and 5 of the W-2 form.
W-2 Box 8: Allocated tips
In addition to reported tips, employers must also report allocated tips in Box 8. The tips designated for tipped employees aren’t considered taxable income. They shouldn’t be included in Boxes 1, 3, 5, or 7.
W-2 Box 9: (Blank)
Leave this box blank.
W-2 Box 10: Dependent care benefits
Dependent care benefits are a type of compensation that employers provide to employees to help cover the cost of care for dependents while they work. These benefits are reported in Box 10.
W-2 Box 11: Nonqualified plans
Nonqualified plans are a type of deferred compensation plan that employers offer to employees. These plans allow employees to defer a portion of their income to a future date, typically retirement. The distributions from these plans are reported in Box 11.
W-2 Box 12: Codes
This box is used to report a variety of different types of compensation, each with a unique code. These codes can represent everything from uncollected Social Security or Medicare tax to the cost of employer-sponsored health coverage.
W-2 Box 13: Checkboxes
Box 13 of the W-2 form indicates specific aspects of the worker’s employment situation. It contains three checkboxes: one for statutory employees, one for retirement plan participants, and one for third-party sick pay.
W-2 Box 14: Other
Box 14 is a catch-all box used to report any other compensation or information not covered in the other boxes.
W-2 Box 15: State | Employer’s state ID number
The state where the employer is located and the employer’s state ID number are entered in Box 15.
W-2 Box 16: State wages, tips, etc.
Box 16 of the W-2 form reports the total taxable wages earned in a specific state. Always consider the specific tax laws of the state when filling out Box 16.
W-2 Box 17: State income tax
Box 17 is reserved for reporting the amount of any state income tax withheld from the employee’s wages.
W-2 Box 18: Local wages, tips, etc.
For employees who pay local income taxes, local wages are reported in Box 18. These are the wages subject to taxation by local jurisdictions, such as cities or counties.
W-2 Box 19: Local income tax
If an employee pays local income taxes, you’ll report the amount withheld from their wages in Box 19. This box is directly related to Box 18 and provides a picture of the employee’s local tax situation.
W-2 Box 20: Locality name
Box 20 provides the name of the locality where the local taxes were paid.
Common mistakes and tips to avoid them
While the process of filling out a W-2 form may seem straightforward, mistakes can happen. These errors can lead to penalties, back wages, and even audits by the IRS. To avoid these issues, it’s important to be aware of the most common mistakes and take steps to prevent them.
One common mistake is using the wrong ink color or font size. Use black ink and ensure your font size fits within the box boundaries. Additionally, always verify the accuracy of the information on the forms before distribution. This includes double-checking all numbers and ensuring names and addresses are spelled correctly.
If an employee reports an error on their W-2 form, it’s crucial to correct it promptly. Employers can often correct submission errors by following these steps:
- File Form W-2 C with the IRS to correct the error.
- Be proactive and meticulous in your tax reporting to avoid common mistakes.
- Ensure your forms are accurate and compliant with the appropriate tax laws.
Filing Form W-2
Once you’ve completed all your W-2 forms, submit them to the IRS and the Social Security Administration (SSA). You must also provide copies to your employees. The deadline for filing W-2 forms is January 31.
You currently have two options for submitting your W-2 forms:
- Electronically: You can file W-2 forms online through the SSA’s Business Services Online (BSO) website.
- Paper forms: If you prefer to submit hard copies, you can order official W-2 forms from the IRS and mail them in.
Each W-2 form consists of multiple copies:
Copy A: Submit this copy to the SSA.
Copy 1: Send this copy to the state, city, or local tax department.
Copy B: This copy is for the employee to file with their federal tax return.
Copy C: This copy is for the employee’s records.
Copy 2: The employee files this copy with their state, city, or local tax return.
Copy D: Employers keep this copy for their records.
W-2 generator by Jotform
While manually filling out W-2 forms can be a tedious and error-prone process, advancements in technology have provided solutions to streamline this task. Jotform’s W-2 generator offers a free, user-friendly online solution for generating and filling out W-2 forms.
Jotform provides an intuitive way to complete W-2 forms on any device, ensuring a responsive and user-friendly experience. The platform prioritizes data security, using GDPR– and CCPA-friendly features, and a 256-bit SSL connection. Users can instantly download their completed W-2 forms as PDFs, saving them time and allowing them to keep their tax documents on file.
In addition to generating W-2 forms, Jotform allows users to transform submissions back into their original W-2 layout, providing a seamless process for tax reporting.
FAQ
When filling out a W-2 form, ensure you use black ink, verify the accuracy of the information, and promptly correct any errors by filing Form W-2 C with the IRS. This can help you avoid common mistakes.
AS ALWAYS, CONSULT AN ATTORNEY BEFORE RELYING ON ANY INFORMATION ON THIS PAGE. THE CONTENT ABOVE IS FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
Photo by Anna Shvets













Send Comment: