An indispensable part of any organization, human resources plays an essential role in the company’s overall success. Whether in a small business or a large enterprise, HR professionals manage important functions like recruiting, hiring, and training. If you don’t already have one, starting an HR department is likely number one on your priority list.
If your human resources department is already up and running, it’s crucial to continuously optimize and improve it so it can better serve your organization. For those planning on scaling operations and growing a business, human resource management can play a lead role in helping attain those goals.
This guide covers the importance of human resource management and how it relates to your business. Take a look at the summaries below for a quick overview of each chapter, then dive into each area for the actionable details you can apply to your organization.
Chapter synopsis
- Introduction.
- Fundamentals of human resource management. A comprehensive HR management system ensures employees have the support they need to thrive. We begin by diving into the key functions of human resource management, such as recruiting and hiring, overseeing leave management, and conducting performance appraisals.
- Understanding human capital management. While the terms are often used interchangeably, human capital management and human resource management aren’t the same. We define human capital management, explain how it differs from HRM, and describe the benefits it offers employers.
- Using strategic human resource management. This area of HRM is all about being proactive and aligning human resources with the organization’s overall goals. You’ll learn the difference between strategic and traditional human resource management, as well as understand transactional HR.
- Merging HRM with high tech. Completing HR functions manually is an ineffective use of time and resources. We cover the benefits of HR management tools and explore the functionality to consider when looking for a human resource management system.
- HRMS in a nutshell. A human resource management system can help your organization automate tasks and improve productivity. We cover the various functions of HRMS that can benefit your organization. Plus, we clarify the difference between HRMS and human resource information systems (HRIS), so you can decide on the right tool for your organization.
- HR automation with forms and workflows. You can complete many human resources tasks without a full HRMS. We’ll show you how Jotform’s automated forms and approval templates provide robust HR functionality your organization can apply right away to save time, reduce errors, and streamline processes.
Next, we’ll set the stage with a broad overview of the fundamentals of human resource management before tackling specifics in later chapters.
Be sure to bookmark this guide for later reference.
Fundamentals of HRM
An integral part of the organization, human resources is responsible for overseeing a range of aspects dealing with employees and their relationship to the employer. Having a clear understanding of the functions of human resource management ensures your business will be able to keep employees satisfied, improve their performance, and reduce turnover.
Recruiting the right employees
One of the primary responsibilities of human resource management is recruiting and hiring the best people for the company. This recruitment process can include advertising open positions on relevant job boards and shortlisting candidates based on applications.
A key element of recruitment is showcasing a company’s value proposition to prospective employees, says Mona Momtazian, director and consultant at the HR consulting firm The Leaders Studio. It’s important to convey how employees will benefit from working for the organization.
After the interview process, HR also does reference and security checks to further vet candidates. They are responsible for drawing up hiring contracts and paperwork, and presenting offers to selected candidates. HR may also be involved with internal recruiting within an organization.
Empowering employees with training
To improve performance, it’s vital to ensure employees have the training and knowledge they need to excel in their roles. One of the key responsibilities of human resource management is overseeing and facilitating employee training.
This can involve researching external training programs and hiring trainers to deliver specific courses. It can also include developing internal training on company-specific processes and leading workshops and seminars.
In addition, the human resources department needs to carefully track which employees have taken specific training and follow up with those who may be lagging. Ensuring employees are well-equipped with knowledge helps lower turnover rates and improve performance.
Conducting performance appraisals
Performance appraisals are an excellent opportunity for managers to provide feedback to employees, learn about potential obstacles they face, and work toward achieving overall company goals.
The HR team is responsible for organizing and setting up performance appraisals at regular intervals. They may draft the initial performance appraisal document, provide schedules for completion, and keep track of employee evaluations. In some organizations, HR may conduct performance appraisals in place of or in addition to the department manager.
Overseeing leave management
Leave management is the process of tracking and approving employee time off in an organization. HR may be responsible for developing time-off policies and may oversee long-term unpaid leave or personal absences.
The human resource management team tracks all time-off requests, grants approvals where needed, and alerts employers about any issues with employees taking too much time off. Typically, the HR team conducts leave management through a human resource management system.
Providing competitive salary and benefits packages
A strategic salary and benefits package is an effective way to attract top-performing employees. However, it’s also a critical component of employee retention, notes Cassandra Rose, partner at Meritarc, a human capital management software platform.
The human resources department researches salaries for each role to determine the best offer the company can provide based on the candidate’s experience and education. They also oversee benefits such as health insurance, time-off policies, 401(k) plans, and more.
In addition, HRM plays a role in making sure employees receive the intangible benefits a company offers, such as an innovative work culture.
Researching and planning for future needs
In addition to short-term and mid-term plans that involve many daily tasks, human resource management specialists also consider the organization’s long-term future. This includes aligning the company’s growth goals with its future hiring goals through forecasting and developing recruitment plans.
In addition to human resource planning, HR also reviews human resource risk management to determine potential weaknesses and issues related to employees.
Effective human resource management needs to be able to evolve with the organization, notes Matthew Burr, a consultant with HR consulting firm Burr Consulting, LLC. In many cases, he says, HR has to evolve faster than the organization to meet its changing needs.
Now that we’ve looked at the fundamentals of human resource management, let’s dive into human capital management and how it differs from HRM.
Human capital management
Many different areas of human resource management focus on specific aspects related to overseeing employees in the workplace. At times, the terms for each area can be conflated or even misnamed. It’s important to understand these different areas of human resource management to effectively use them in your organization.
One of the often misunderstood terms is human capital management — which is sometimes used interchangeably with human resource management.
What is human capital management?
Human capital management, not to be confused with human resource management, is all about maximizing the ROI from a company’s employees. The “capital” in human capital management refers to the economic value employees can bring to the company with their education, experience, networks, expertise, and skills.
“Human capital management is all about seeing the unique aspects of your workplace population,” says Rose. This area of human resource management is relatively new, having emerged in the last few decades.
The goal of human capital management is to maximize the business value that employees bring to a company. This provides businesses with a competitive advantage and helps them control more market share.
By effectively acquiring, managing, and developing the workforce, businesses can realize more value from their employees. Managing a company’s human assets effectively also improves its bottom line, explains Jim Cichanski, founder and CHRO of Flex HR, an HR consulting and outsourcing firm.
Initiatives that fall under the human capital management umbrella can include
- Developing a clear organizational mission, vision, and values statement
- Implementing actionable employee onboarding and training programs
- Creating a workplace culture where employees can thrive
- Reorganizing departments in innovative ways to help employees do their best work
- Ensuring employees understand the organization’s short-term and long-term goals
- Developing workflows, processes, and systems to optimize employee productivity
Human capital management vs human resource management: Key differences
It’s true that human capital management and human resource management are quite similar and have many overlapping elements. However, these terms shouldn’t be used interchangeably because they don’t refer to the same processes.
The key difference in human capital management vs human resource management is the ultimate goal.
The goal of human capital management is to achieve the greatest ROI from the company’s employees, while the goal of human resource management is to effectively manage the systems, processes, and regulations that enable employees to succeed at their jobs.
In large companies, many organizational leaders take part in human capital management, not just those within the HR department. However, human resource management is typically only handled by the HR team.
Human resource management includes elements like payroll, benefits, time-off policies, and performance appraisals, which can help support human capital management in meeting its goals.
The benefits of human capital management
An organization’s most valuable asset is its employees, and the human capital management approach looks at maximizing those resources to realize their full potential. Not only are employees valuable, but they are also the most expensive assets of an organization, explains Burr.
Ensuring company leadership effectively manages employees and provides them with a welcoming and encouraging workplace culture is key. This not only benefits the company as a whole but also positively impacts the employees themselves.
Benefits of human capital management include
- Better productivity. When an organization focuses on supporting and optimizing the skills, expertise, and knowledge of the workforce, it can perform more effectively and meet schedules and targets.
- Lower turnover. Human capital management engages employees on a deep level by making sure they understand the organization’s mission, values, and goals. This creates a sense of loyalty and personal investment. Rose notes that fill times for open positions can last between three and six months. Lowering turnover means spending less time on recruiting, hiring, and onboarding and more time developing existing employees.
- Improved customer experience. When employees thrive, customers reap the benefits. Human capital management fuels innovation, which leads to more effective products and services that meet customer needs.
Now that you understand the basics of human capital management, let’s explore another area of human resources — strategic human resource management.
Strategic human resource management
A contemporary area of human resource management is strategic human resource management. As the name suggests, strategic human resource management is all about developing HR initiatives and working to attain specific strategic company goals.
Whether your organization is a global enterprise or a small business, strategic human resource management can help you meet company objectives more effectively.
What is strategic human resource management?
Strategic human resource management is a modern approach to HRM that involves focusing on long-term company goals and aligning HR initiatives to achieve them effectively. For example, if the company’s five-year plan is to grow the manufacturing arm, then the strategic human resource management approach may involve hiring 10 new manufacturing employees each year.
This area of HR also focuses on data and depends on analytics to inform important decisions. For instance, if the company has internal training programs, the strategic HR team may look at the results of these programs to see if the information is actionable in the workplace — and make changes to improve the sessions accordingly.
Considering all HR stakeholders is also a critical element of strategic human resource management. In addition to employees, other stakeholders may include partners, customers, investors, and government agencies.
The strategic human resource management approach ensures that HR strategy is aligned with these stakeholder needs as well — not just those of employees. It’s also important for HR to look outside their department. Burr notes that strategic HR management should involve all areas of the business, including finance and operations.
This proactive approach to human resource management can help organizations save considerable time and money on recruitment and other HR activities, says Momtazian. It can also create opportunities for an organization to reduce the time it takes to meet business objectives.
Momtazian explains that taking a strategic approach leads to more positive outcomes for the entire company.
Traditional vs strategic human resource management
What’s the key difference between traditional and strategic human resource management? According to Rose, the traditional approach is reactive while the strategic approach is proactive.
For example, in a traditional HRM model, the HR department will post open positions once the department manager indicates the positions need to be filled. However, with a strategic approach, the HR manager and the department manager will be aligned in their hiring needs and long-term plan and will recruit based on the company’s growth strategy.
Similarly, with a traditional approach, the HR department may answer employee questions about benefits and policies. With a strategic approach, the HR department will create a detailed employee handbook, provide onboarding training, and offer regular sessions for employees who want to learn more about specific workplace benefits and policies.
Taking a proactive approach can greatly benefit an organization because important initiatives aren’t left to the last minute. When a long-term plan is in place, the human resource department is better prepared to support all employees and help the company achieve its major objectives and targets because they are thinking ahead, notes Rose.
What is transactional HR, and when do you need it?
A related area of human resource management is transactional HR, which is a task-oriented approach to human resources.
Instead of focusing on long-term goals like strategic HR or reacting to organizational needs like traditional HR, transactional HR is about completing day-to-day tasks. It overlaps with both strategic and traditional HR approaches and can be done in conjunction with either approach.
Examples of transactional HR tasks include
- Administrative tasks, such as creating and distributing forms and documents
- Creating job descriptions and posting open positions
- Completing payroll documentation
- Tracking employee time-off requests
- Documenting workplace conflicts and issues
- Facilitating performance appraisals
If a company wants to focus more on strategic human resource management, outsourcing transactional tasks is an effective way to go about it, Cichanski explains. This way, the team can concentrate less on tedious manual tasks and more on strategic activities.
We’ve covered two more approaches to HR: strategic human resource management and transactional human resources. Now, it’s time to see how technology can benefit human resources processes.
Merging HRM with high tech
Whether your organization has five employees or 500, there are many moving pieces to keep track of as part of human resource management.
Taking a manual approach is time-consuming and can lead to missed opportunities and errors. To streamline human resource management, it’s vital to implement tools that can help save time, improve productivity, and provide better support to stakeholders.
The benefits of HR management tools
A wide range of available HR management tools can provide numerous advantages based on the company’s intended outcomes.
Take the recruitment process as an example: An automated job application that allows HR to compare candidates’ answers is an effective way to find the best applicant for the job. Using videoconferencing software to conduct interviews is an excellent method to reach candidates who can’t meet in person, saving the organization time and resources.
The benefits of HR automation include
- Centralized data and information. Instead of storing personnel documents in a filing cabinet, a software solution ensures the HR team can access employee information anywhere, anytime. This data is then at HR’s fingertips, which increases productivity.
- Improved security. Organizations must protect employee data, and many HR management tools provide increased security. This puts both employees and employers at ease because they know unauthorized parties can’t access this information.
- Better data management. Whether tracking employee-time off requests or training completions, automated HR systems make it easier to monitor, track, and analyze employee-specific data. When taking a strategic approach, they also enable HR to compare data from year to year to see improvements and changes. Data integrity is critical to ensure you have basic contact and emergency information for all employees. One of the key benefits of an HR management system is accuracy of information, says Cichanski, since an automated approach reduces the chances of human error.
- Enhanced employee experience. Employee-facing tools like learning management systems and self-serve document systems give employees more control. They can access information without having to rely on others.
Finding the right HR management tools for your business
With a plethora of available human resource management tools, there are plenty of options to choose from. Whether you’re looking for the best HR management tools for large companies, the best HRM software for small business, or alternatives to popular HR solutions like ADP, here’s what to consider:
- Determine your critical requirements. Have a brainstorming session with the important stakeholders within and outside of HR to determine which functionality is an absolute must and what’s nice to have. Be sure to consult IT teams and leadership executives.
- Focus on accessibility. Will your team need access to the system from work, home, the road, or a client’s office? Will they want to use it on mobile devices or just on desktops?
- Keep an eye toward growth. Burr emphasizes the ability to scale. Your technology solutions should be able to grow and evolve with your organization.
- Make the user experience a priority. Consider how much training employees will need to learn the tool and whether it’s intuitive. Is it convenient for employees to use a self-service model?
- Remember compliance. Be sure to consider whether the HRM system can accommodate the compliance regulations and data protection rules for the specific locations where your business has employees.
- Look at all options. While there are many leading HR management tools, there are also newcomers to the market. For example, don’t be afraid to investigate ADP alternatives or substitutes for BambooHR if those don’t meet your requirements and budget.
How HR automation can help your organization
HR automation can improve most human resources processes. By eliminating tedious manual tasks, organizations can spend more time on strategic initiatives. Some of the most common tasks that HR can streamline include
- Getting electronic signatures on contracts and forms
- Collecting new hire data
- Scheduling recurring shifts
- Tracking time-off requests
- Monitoring petty cash expenses
- Keeping employee training checklists
- Managing onboarding workflows
With a strong grasp of how technology can benefit human resource management, it’s time to look at the different kinds of human resource management systems.
HRMS in a nutshell
Human resource management tools and software are collectively referred to as human resource management systems (HRMS). Accessible by both the HR department and employees, these systems automate tasks, secure data, and centralize important information.
What is HRMS?
You may be asking, “What is an HRMS, and how should you choose one?” HRMS is a software solution that can help human resource teams manage specific HR functions like hiring candidates, managing payroll, overseeing time-off requests, or a combination of activities.
In some organizations, HR departments complete these tasks manually; however, an HRMS can improve the processes, reduce errors, and increase productivity in many cases. Before converting to an HRMS, it’s important to consult IT and leadership stakeholders, as well as HR, to help determine your company’s technology needs, says Burr.
If you’re dealing with any of these issues, consider switching to an HRMS:
- Tedious clerical and administrative tasks are taking time away from more strategic or long-term initiatives
- Compliance or security breaches risk exposing confidential employee information
- Employees work remotely or in geographically dispersed office locations, making it difficult to share HR documentation
- Employees lack self-serve options to access information about company policies, processes, and procedures
- Employee data is frequently inaccurate, incomplete, or missing
- Human resources employees have more tasks and activities than they can manage and need ways to improve overall productivity
Important functions of an HRMS
Some human resource management systems are comprehensive tools with different modules that coincide with related HR areas. For example, one solution may have a module for payroll, a module for scheduling requests, and a module for performance appraisals.
Other human resource management systems focus on one specific HR area, such as benefits administration or learning management.
Common employee-related functions of an HRMS include
- Recruitment and application processes
- Storing confidential information
- Onboarding workflows
- Attendance and time-off tracking
- Scheduling
- Performance appraisals and self-appraisals
- Payroll processing
- Training and learning management
- Benefits administration and tracking
- Self-service tools
- Systems analytics
Keep in mind that a single HRMS may not cover all of these functions; you may need to integrate multiple systems to create a customized solution that works best for your organization. Be sure to identify the human resource processes you want to automate and streamline to find a system or systems that will help you reach your goals.
Cichanski explains that HR technology not only automates administrative functions but also assists the HR team in developing more accurate and complete information. This is key when deciding which functionality you want in an HRMS.
HRMS vs HRIS: Key differences
When discussing human resource management systems, you may hear the term human resource information system (HRIS) used interchangeably. While these systems are closely related and people sometimes conflate or misuse the terms, there are some notable differences. Human resource information systems are a subset of human resource management systems.
Typically, an HRMS has more robust technology that offers several functional solutions. An HRIS typically focuses more on tracking numerical data and important employee information like birth dates and social security numbers.
An HRIS deals mostly with quantitative features, such as tracking data for compensation or benefits or managing specific payroll tasks. While an HRMS can manage all of these functions, they also handle more qualitative functions, such as employee satisfaction, onboarding, recruitment, and learning management.
Organizations that want to streamline quantitative functions typically use an HRIS, while those that want to improve both quantitative and qualitative functions choose an HRMS.
Next, let’s look at how you can automate HR processes with Jotform workflows and forms.
HR automation with forms and workflows
The benefits of HR automation are clear: Save time and money while improving productivity and performance. However, with so many human resource management system options available, it’s hard to know where to begin.
Keep in mind that you don’t need to use specialty HRMS software — forms complete many of the same functions with ease. You can use Jotform as a robust human resource management system to automate a range of HR processes.
Using Jotform forms to automate HR processes
No matter the size of your organization, many human resources tasks require candidates or employees to fill out HR forms. Whether you’re collecting numerical data like social security numbers or qualitative data like answers to interview questions, automated forms can make it easy to track, monitor, and revisit information.
Here are several ways Jotform can help automate HR forms:
- Job application forms. With over 250 job application form templates, it’s easy to find one that suits your organization’s needs. Collect and view candidates’ experience, resumes, cover letters, and contact details with these Jotform templates.
- Employee information forms. Once you’ve hired a candidate, HR needs to gather details like contact information, medical history, and more during the onboarding process. Jotform has over 190 employee information form templates to easily customize or integrate with tools like Google Sheets and Airtable. Momtazian notes that employee onboarding is one of the easiest functions to automate with HR technology.
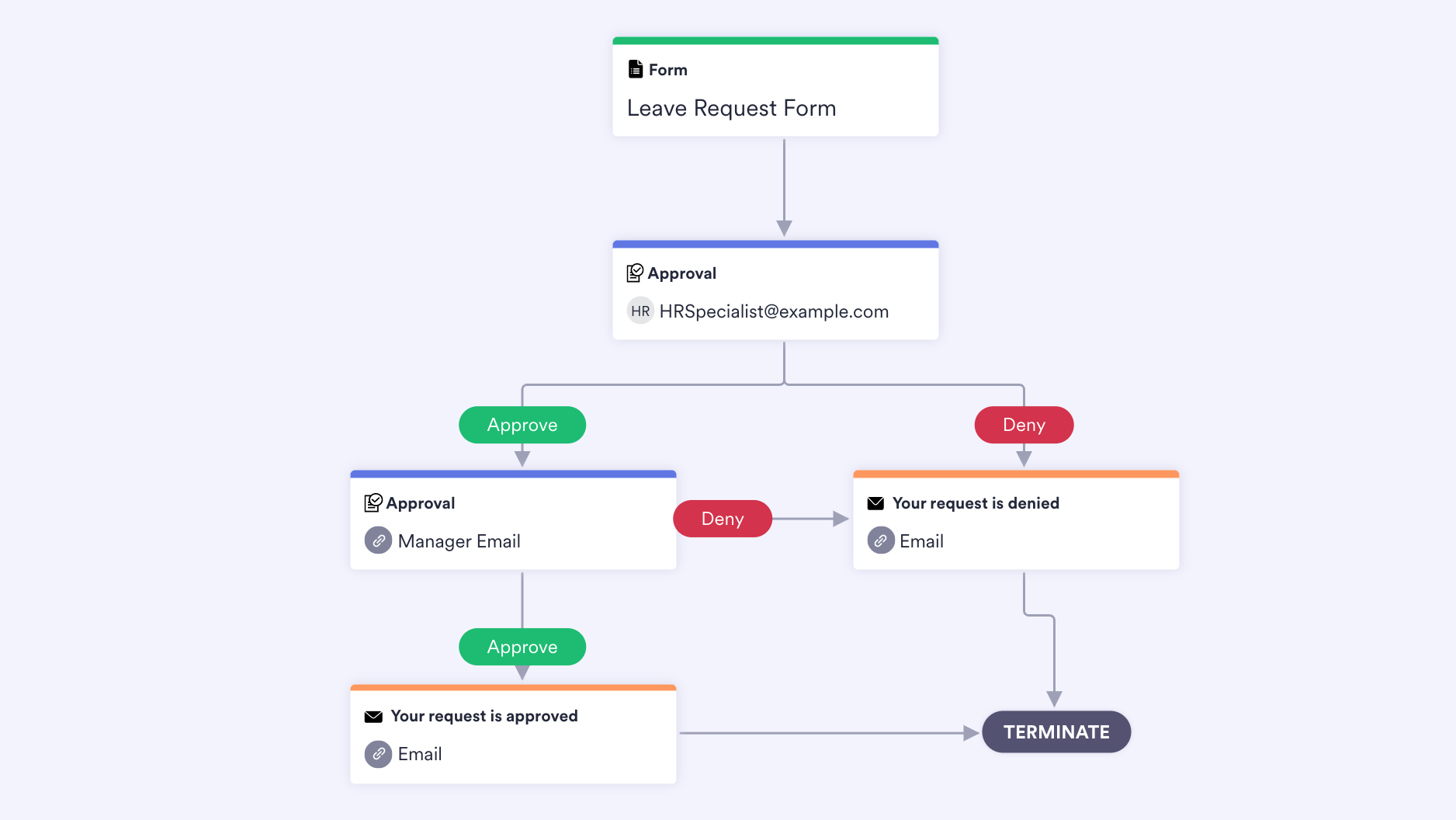
- Leave request forms. Taking time off to reenergize is a must, and Jotform offers several leave request form templates to make recording that time away easier through customization and integration with Google Sheets. Cichanski notes that many organizations still manually calculate PTO. Automating this administrative task can allow human resource management to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Implementing Jotform approval templates to streamline HR functions
Having a manager or human resource team member sign off on approvals for specific processes is a necessity. However, using email or messaging systems for approvals can be haphazard and difficult to track. Consider building automated approval workflows with Jotform’s approval templates.
Jotform has more than 100 approval templates ready to go for the most commonly used HR processes. Here are a few examples:
- Leave request approvals. When an employee requests time off, they can automatically send the request to the appropriate person to approve or deny the leave.
- Travel expense reimbursement approvals. You can set travel expense approval workflows based on how much the employee spent. For example, if the employee spent over $500, the request is automatically sent to the finance manager.
- New hire approvals. You can create a complex hiring approval workflow based on hiring criteria with automated emails, conditional logic, and due dates.
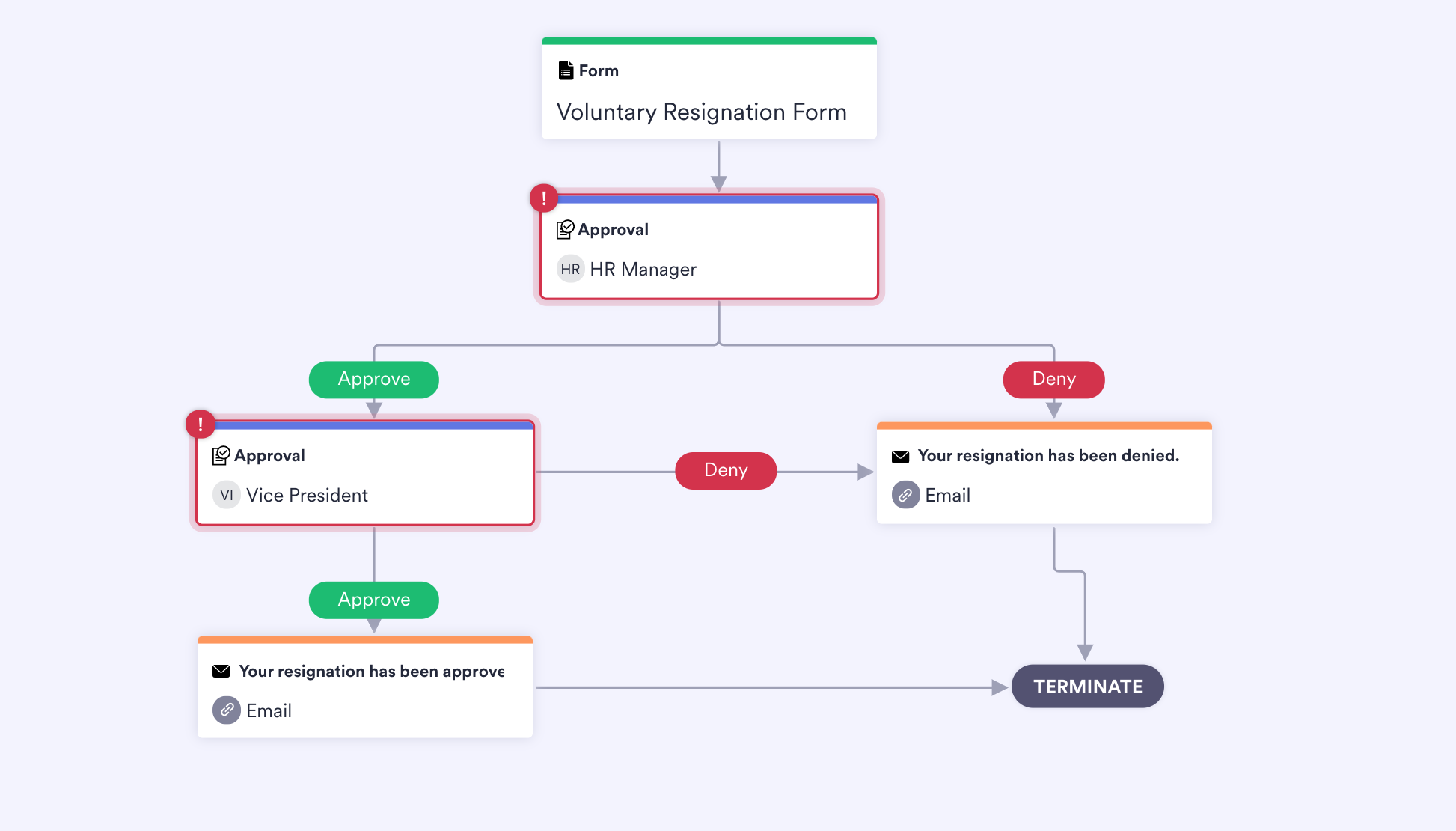
- Employee resignation approvals. When an employee resigns, they can send the request through the proper channels to ensure both the employee and HR document and approve the process.
Conclusion
Human resource management is an integral part of any organization — whether you have a handful of employees or several hundred. Performing many important functions like hiring, onboarding, training, and performance appraisals, human resource management professionals ensure employees can help the organization reach its goals.
There are different approaches to human resource management, such as human capital management, strategic human resource management, and transactional human resources. Each approach plays a unique role in supporting employees and employers.
Be sure to streamline your human resource management processes with the right tools. Human resource management systems and human resource information systems can help collect, track, monitor, and analyze quantitative and qualitative data to improve productivity and employee sentiment. Last, using HR automation forms and workflows can save time and reduce manual errors.
Meet your human resource management guides
Cassandra Rose
Cassandra Rose, a partner at Meritarc, has over 15 years of HR experience. She is certified as a Senior Professional in Human Resources (SPHR, SHRM-SCP) and holds a B.B.A. in business management, a master’s degree in human resources and employment relations, and a professional certificate in diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI). Having held roles at multibillion-dollar global brands and unicorn startups, Rose has developed proven strategies that positively impact employees’ physical, mental, and financial wellbeing and guide organizations committed to DEI to embed equitable practices.
Jim Cichanski
Jim Cichanski is the founder and CHRO of Flex HR, which is in its 21st year as an HR consulting and outsourcing firm. He has over 40 years of experience as a professional HR practitioner. Cichanski has provided HR support to both large Fortune 500 companies and hundreds of mid-size companies, and assisted organizations in over 400 mergers and acquisitions.
Matthew Burr
Matthew Burr is an HR consultant at Burr Consulting, LLC, with over 14 years of experience in the HR field. He currently works with small and medium-sized organizations on strategic HR issues. Burr is also an assistant professor of business administration at Elmira College.
Mona MomtazianMona Momtazian, director and consultant at The Leaders Studio, advises executives to teach people to like change and recruit best-fit employees to lead it. Momtazian has been in the organizational development (HR, change management) space for over 20 years and can identify the best-fit candidate for a senior role, offer coaching on how to lead change successfully, and identify the systemic and root causes of people issues and opportunities to support organizations in achieving strategic objectives.









































Send Comment:
2 Comments:
More than a year ago
thank you
More than a year ago
The extra efforts you put into this article reflect your incredible leadership skills. My best wishes. Love to read all your articles in future. Do visit my website